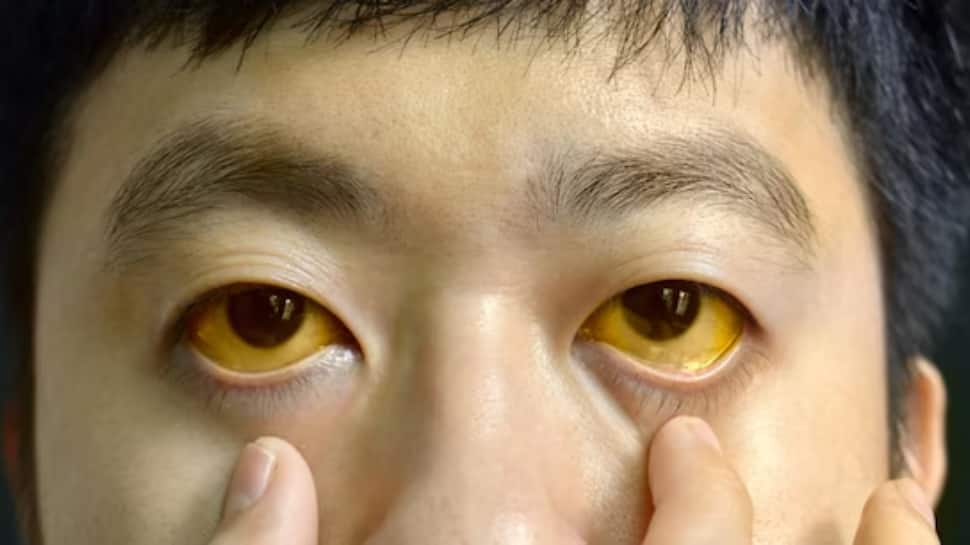
Jaundice is a condition characterised by the yellowing of the skin and eyes due to the buildup of bilirubin, a yellow pigment produced during the breakdown of red blood cells. While mild jaundice can sometimes be harmless, persistent or severe jaundice may indicate underlying health problems that require medical attention. Understanding its causes can help you take timely action.
1. Hepatitis (Viral Infection)
One of the most common causes of jaundice is hepatitis, an inflammation of the liver caused by viruses such as Hepatitis A, B, or C. These infections interfere with the liver’s ability to process bilirubin, leading to its accumulation in the body. Symptoms may also include fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, and dark-colored urine. Early detection and proper treatment are crucial to prevent liver damage.
2. Gallstones and Bile Duct Blockages
Gallstones or obstructions in the bile ducts can prevent bile from leaving the liver and entering the digestive system. Bile contains bilirubin, and when its flow is blocked, bilirubin builds up in the bloodstream, causing jaundice. Individuals may experience severe abdominal pain, vomiting, and pale stools. In such cases, medical procedures or surgery may be required to remove the blockage.
3. Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
Excessive alcohol consumption can damage liver cells over time, leading to alcoholic liver disease. This reduces the liver’s capacity to process bilirubin efficiently, resulting in jaundice. Other symptoms often include swelling in the abdomen, fatigue, and confusion in severe cases. Cutting down on alcohol and seeking medical care early can help prevent permanent liver damage.
4. Hemolytic Anemia
Hemolytic anemia is a condition where red blood cells are destroyed faster than the body can produce them. The excessive breakdown of red blood cells leads to increased bilirubin levels, causing jaundice. People with this condition may also notice symptoms like dark urine, fatigue, and a rapid heartbeat. Treating the underlying cause of anemia is essential to manage jaundice effectively.
5. Liver Cancer or Cirrhosis
Chronic liver conditions, including cirrhosis and liver cancer, can impair liver function and cause jaundice. Cirrhosis, often due to long-term liver damage, leads to scarring that reduces liver efficiency. In liver cancer, the growth of tumors can obstruct bile flow. Both conditions require urgent medical evaluation, and symptoms may include unexplained weight loss, abdominal swelling, and persistent fatigue.
Jaundice is more than just a cosmetic concern—it often signals an underlying health issue that shouldn’t be ignored. By understanding its major causes, from liver infections to bile duct blockages, you can stay alert to early warning signs and seek timely medical care. Remember, prompt attention not only helps treat jaundice effectively but also protects your overall liver health. Don’t wait—listen to your body and act early.
(This article is meant for informational purposes only and must not be considered a substitute for advice provided by qualified medical professionals.)